OEM:
BHA437140
Compatible Vehicles:
Mazda: Mazda 6 (CN) 2018/01-2021/12
Mazda: Mazda 2 (CN) 2014/06-2015/12
Mazda: CX-9 (CN) 2013/01-2019/12
Mazda: Mazda 3 (CN) 2011/01-2013/12
Mazda: CX-9 (CN) 2007/01-2012/12
Mazda: CX-5 (CN) 2017/01-2020/12
Mazda: CX-3 (CN) 2016/01-2020/12
Accessory Construction:
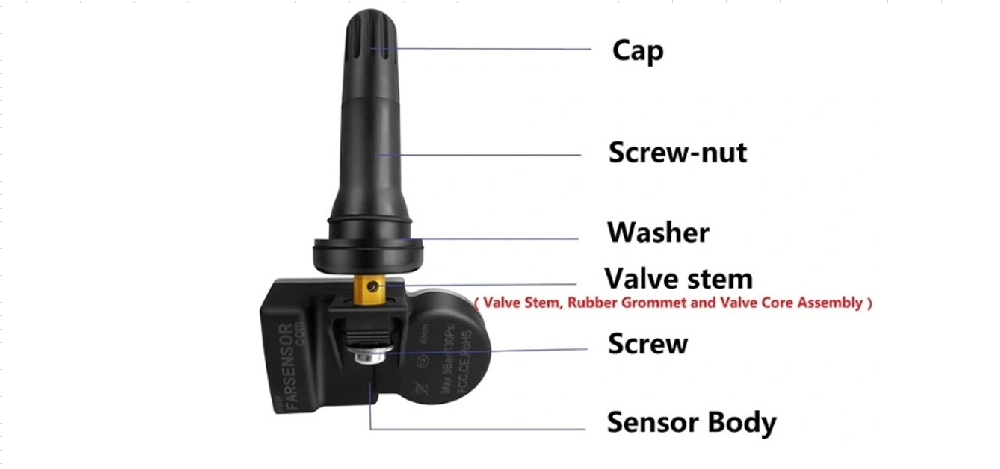
A tire pressure sensor, also known as a tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) sensor, is a device used to monitor the air pressure inside a vehicle's tires. It is an essential component of modern vehicle safety systems, helping to ensure proper tire inflation, which is crucial for optimal vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. Here’s a detailed description:
Components and Functionality
Sensor Unit:
Pressure Sensor: Measures the actual pressure within the tire.
Temperature Sensor: Some advanced sensors also measure the temperature of the air inside the tire, as temperature can affect pressure readings.
Transmitter: Sends the pressure data to the vehicle’s onboard computer or a dedicated TPMS receiver.
Types of TPMS:
Direct TPMS: Uses sensors mounted directly on the tire valve or inside the tire to measure the exact air pressure. Each sensor communicates wirelessly with the vehicle’s computer system.
Indirect TPMS: Estimates tire pressure indirectly by using the wheel speed sensors of the anti-lock braking system (ABS). It detects differences in rotational speed between tires to infer pressure loss.
Power Source:
Most TPMS sensors are battery-powered, with a lifespan typically ranging from 5 to 10 years. Some advanced systems can harvest energy from the tire’s motion.
Data Transmission:
The sensor transmits data wirelessly to the vehicle’s onboard computer. The data is often displayed on the dashboard, alerting the driver to any pressure anomalies through visual (light indicators) and auditory (warning beeps) signals.
Benefits
Safety: Proper tire pressure ensures optimal contact between the tire and the road, enhancing braking performance, handling, and overall vehicle stability.
Fuel Efficiency: Correct tire pressure reduces rolling resistance, which can improve fuel economy.
Tire Longevity: Maintaining the correct pressure helps prevent uneven tire wear, extending the lifespan of the tires.
Environmental Impact: Properly inflated tires contribute to better fuel efficiency, thereby reducing carbon emissions.
Maintenance
Regular Checks: Even with TPMS, it's important to manually check tire pressure periodically, as TPMS sensors can sometimes fail or provide inaccurate readings.
Sensor Replacement: TPMS sensors typically need to be replaced when their batteries die or when they are damaged. Some systems allow for battery replacement, while others require the entire sensor to be replaced.
Common Issues
Sensor Failure: Sensors can fail due to battery depletion, damage from road debris, or corrosion.
Interference: Wireless signals from the sensors can sometimes be affected by external electromagnetic interference.
Calibration: After tire rotation, replacement, or repairs, TPMS sensors often need to be recalibrated to ensure accurate readings.
Overall, tire pressure sensors are a critical component of vehicle safety systems, providing real-time monitoring and alerts to help drivers maintain proper tire pressure, ensuring safety, efficiency, and performance.
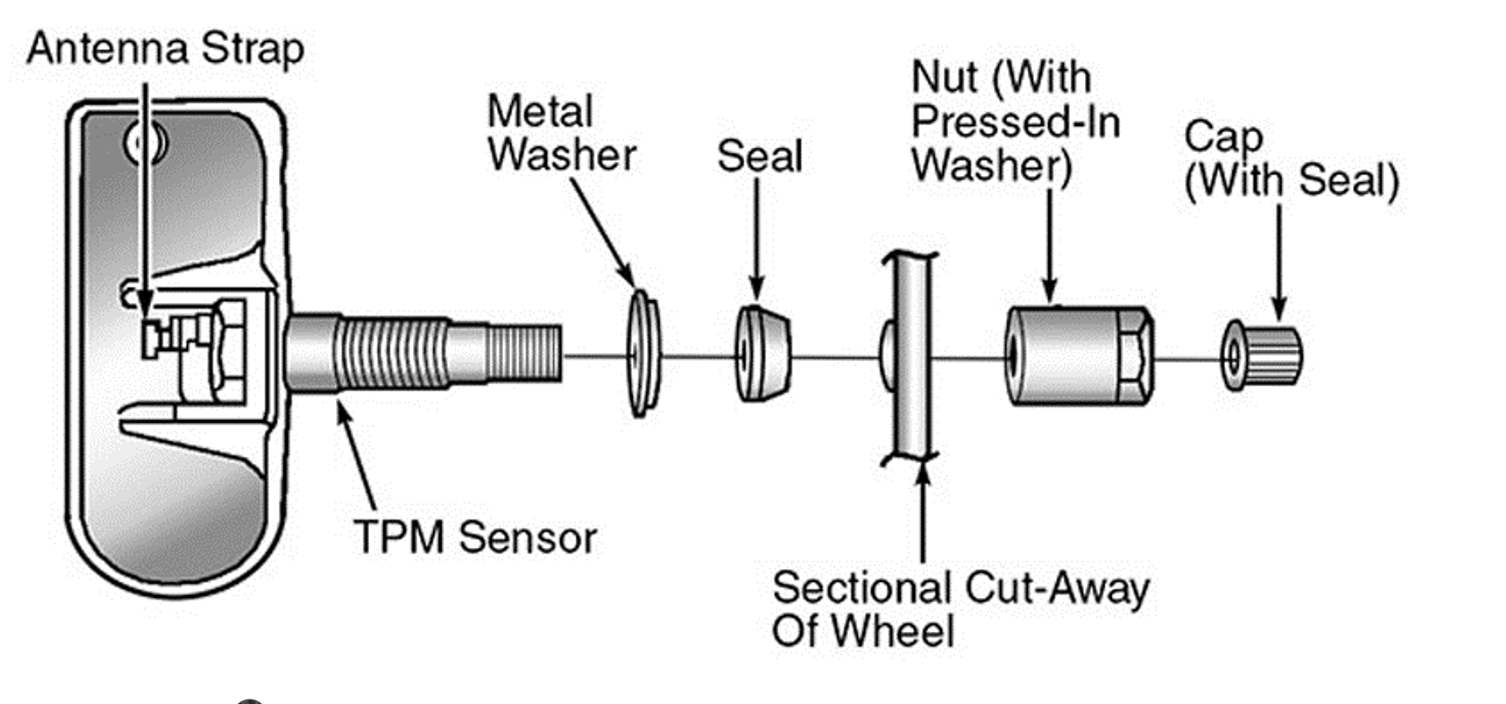
Tips and Warnings
Safety First: Always wear appropriate safety gear and follow safety procedures when working on a vehicle.
Check the Manual: Consult your vehicle’s owner manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
Professional Help: If you are unsure about any step, consider seeking help from a professional mechanic.
By following these steps, you can replace a tire pressure sensor and ensure your vehicle's TPMS is functioning correctly.



